Startup Layoff phenomenon extends across diverse industries. The current business ecosystem is becoming more dynamic as more startups appear. Startups are the key draw for people pursuing professions due to their comparatively higher growth rates than those of more established businesses. But the adoption of daring ideas, rapid growth, and innovation are typically associated with a startup’s success in an ecosystem. This is connected to how these startups are moving in the direction of scaling up so that they can grow. In terms of firm size scaling up, execution of marketing strategy, profit conversion, and management of capital funds, many startups cannot endure this quick development.
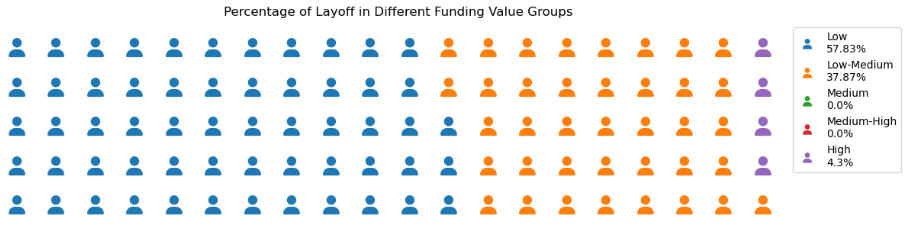
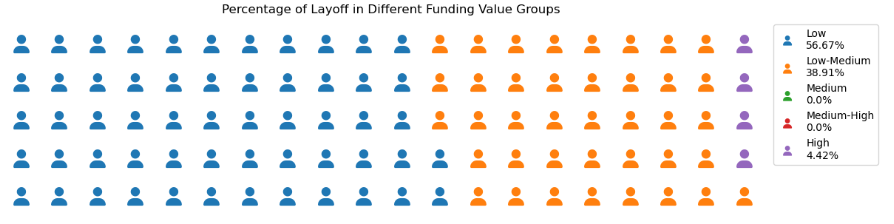
Based on the data provided (Startup Layoff Percentage 2020-2023), it can be seen that 57.83% of startups with a funding range of $0-$20 billion have laid off employees. Similarly, 37.87% of startups that fall within the $20 billion to $40 billion budget range have laid off employees. In contrast, startups in the $80 billion to $121 billion funding range have a much lower layoff rate of just 4.3%.
The Scatter Plot of Layoff Percentage Vs Total Fund Raised
Is this correlation tied to financial stability, strategic decision-making, or market positioning that remains relatively fragile? This could be the reason why startups with modest funding are more susceptible to employee layoffs compared to their counterparts with considerably larger funding allocations. Delving deeper into the analysis reveals the necessity for a comprehensive understanding of additional variables such as industry-specific influences, the impact of investor expectations, efficient resource allocation, and various other contributing factors. In this article, I will narrow my focus to examining the intricate connection between layoff rates, the specific industry context, and funding values.
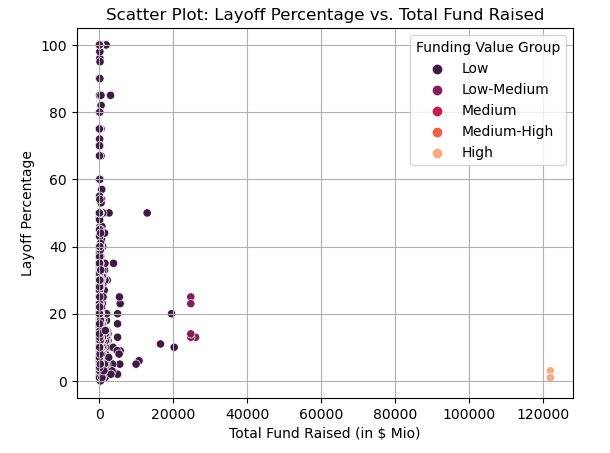
Let’s see the relationship between the layoff rate and funding value in the scatter plot visualization. The accompanying chart illustrates that startups with lower funding values tend to exhibit a higher susceptibility to employee layoffs, indicating a heightened level of risk.
Note Funding value : Low ($0-$20Bio), Low-Medium ($20Bio-$40Bio), Medium ($40Bio-$60Bio), Medium-High ($60Bio-$80Bio), High ($80Bio-$121Bio)
*Startup Layoff Percentage 2020-2023
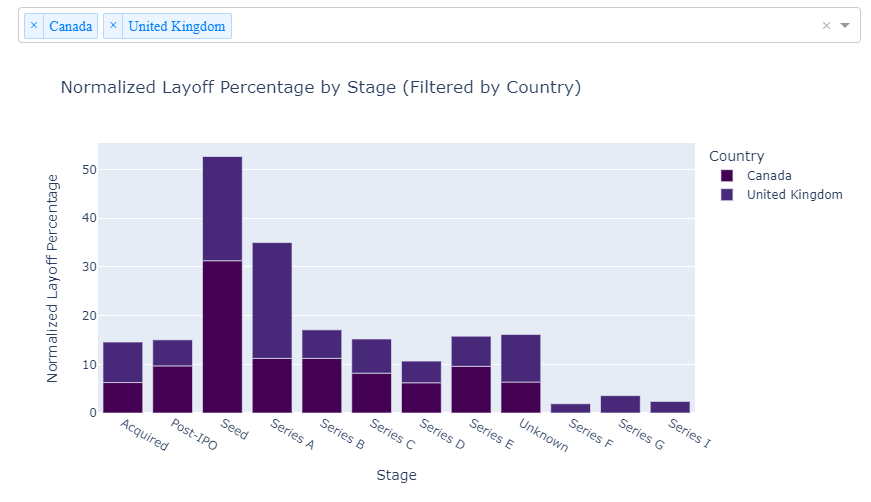
Startup Layoff by Country (Interactive Dashboard)
The recent trend of layoffs observed across numerous startups worldwide is noteworthy. To gain insight into the distribution of startup layoffs in various countries, explore the interactive dashboard provided below. The evident trend shows that startups implementing employee layoffs are widespread across multiple countries. However, these layoffs appear to be more frequent in European nations. This could potentially be attributed to the substantial quantity of startups in Europe compared to other regions. For detailed insights pertaining to each specific nation, kindly choose the desired country from the list provided in the “Highlight Country” column.
Let’s explore the interactive dashboard offered below for a more thorough grasp of this persistent trend in layoffs. This dashboard allows for a comparison of the layoff percentages among companies at different funding stages across various countries. To facilitate cross-country comparisons, simply select the countries of interest in the “Country Filtered” column.
As an illustrative example, we’ll focus on data and comparisons between Singapore, Indonesia, and the United States. Highlighting that startups in these countries, particularly those in the series-B funding stage, are actively engaging in layoffs.
To analyze the startup layoff phenomenon on a country-by-country basis, we can approach it from an industry standpoint. For instance, in Canada, a noteworthy instance of employee layoffs occurs within the healthcare industry. In contrast, both the United States and India display a propensity for layoffs in the finance sector. In Indonesia, the transportation industry emerges as a prominent contributor to layoff percentages.
This variation indicates that the causes behind startup layoffs in each country are distinct. When observed from an industry perspective, a prominent factor likely revolves around the individual country’s market conditions and startup ecosystem. These elements play a pivotal role in shaping the dynamics of the layoff phenomenon.
Closing Thoughts
To wrap up this analysis, let’s outline the key findings. The occurrence of the layoff phenomenon within startups worldwide is prevalent in startups with middle to low funding values. To be precise, startups with funding below $40 billion demonstrate a higher tendency to undertake employee layoffs. Notably, the specific industry sectors impacted by this phenomenon vary across countries, contingent upon the distinctive dynamics of each market and the local startup ecosystem.
Further analysis is imperative to ascertain the underlying reasons driving startups to implement employee layoffs. For a comprehensive view of the data analysis and visualization code, kindly refer to my Kaggle profile linked here. Additionally, you can visit the post related to the code here.
If you be interested in collaboration related to data analytics and business strategy consultation, don’t hesitate to reach out via email. Your support is greatly appreciated – consider fueling my efforts by buying me a coffee here.